Osteochondrosis degenerative-dyclic disorders in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral joints, causing deformation and destruction.Osteochondrosis can occur in one or more spines.The cervical region osteochondrosisIt occurs especially often and sometimes causes very serious complications.
Characteristics of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Due to the properties of the cervical spine structure, osteochondrosis in this segment has many properties and symptoms of osteochondrosis.The cervical spine consists of small movable vertebrae, which are constantly subjected to significant and long loads.The spinal canal is the narrowest in the cervical region, so the spinal cord compression is much more common in this segment and leads to quite serious injuries.There is a large neck of nerve endings and blood vessels, including the spine artery, which provides the nutrition of the porridge, the oblong brain and the brain.Blood flow violations in this artery reduced coordination, dizziness, reduction of vision and hearing, and in severe cases stroke can occur.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The cervical region osteochondrosisThe spine manifests itself with multiple syndrome:
-
Reflex and irritable syndrome
Burning pain in the cervix and consuming region, which after sneezing, suddenly movement of the head or a long static condition such as sleep or fixed condition, as well as the head or neck later, -often complaints with the cervical spine osteocondrosis.Pain can radiate to the shoulder or chest cage. Spinal Channel Reducing Syndrome (Stenosis of the Spinal Channel)
This syndrome is as a result of the compression (tightening) of the spinal cord and vessels, which leads to circulatory disorders and the development of myelopathy in the affected area - a rare but most frightening complication of osteochondrosis.Vertro -carbon cervical myelopathy is primarily found in middle and elderly persons with the spinal cord or vessels with the rear osteophytes, the thickened yellow ligament, and the intervertebral disks hernia.The disease is gradually evolving, initially in the cervical spine, restrictions of pain and movement are often observed.In the future, cervical osteochondrosis can cause impaired functions of the upper and/or lower limbs, numbness, feeling of tingling fingers, feelings of cotton legs or arms, parachis and paralysis.-
Coordinated syndrome
The manifestation of the radicular syndrome in the osteochondrosis of the cervical spine depends on which nerve root arises as a result of structural changes in the plate.In any case, however, the cervix osteochondrosis occurs with a headache that is painful, pulsating or burning, sometimes flowing in the type of hypertension.Back pain is rarely local and usually gives the blades, forearms, shoulders and/or hands to the fingers of the brush.
Depending on the segment of the affected spine may include the following symptoms:
- C1-C2: In this segment, defeat usually occurs as a result of automotive injuries, and fragrance and speech violations, face and sublingual muscles hypotropy, and a reduction in sensitivity in the occlital region.
- C2-C3: It also rarely affects it and is accompanied by reducing, visualization and sensitivity and sensitivity of the muscles of the tongue, which leads to a speech disease and a sense of taste, and the appearance of inflammation, sweating or the appearance of sore throat.
- C3-C4: Because the diaphragmatic nerve retires in this segment, besides the pain of the wrist and shoulder gpu, the spam of the belt and the trapezoid muscles, the right hypochondrium pain and the heart also develop, and breathing movements are disturbed.In addition, gundishness, nasal congestion, snoring, decrease in scent, reduction of the sagging muscles of the face, and deterioration in the condition of the teeth.
- C4-C5: In this segment, the defeat is accompanied by painful feelings in the shoulder shoulder, the deltoid muscle hypotrophic, a reduction in the sensitivity of the exterior of the shoulder, a reduction in shoulder and skeletal inflammation in this area.Other symptoms may occur in the sound change, the feeling of inflammation in the larynx, snoring.
- C5-C6: The segment is most commonly sensitive to degenerative-dynamic lesions and has extensive symptoms.Above all, pain and impaired skin sensitivity from the shoulder blade, the outer surface of the shoulder to the radial surface of the forearm and the thumb of the hand.Subsequently, somatic symptoms develop, including the treatment of lungs and bronchi frequently and poorly, including asthma, rheumatic and allergic manifestations, and angina pectoris symptoms.
- C6-C7: The lasion of the nerve in this segment leads to the appearance of pain in the scapula in the scapula, on the back of the forearm to the back of the hand.In addition, damage to this segment accompanies symptoms corresponding to thyroid disease, mediastinal organs and cardiovascular system.
- C7-T1: The lesion of the C8 spine is accompanied by the hypertrophy of the three-headed muscle and the different small finger, leading to the weakening and pain of the bending reflex with the skin, shoulder, shoulder blades, elbow joint and small finger sensitivity.In severe cases, symptoms may develop such as angina pectoris, arrhythmia and asthma.
-
Cardial syndrome for cervical osteochondrosis
Cardial syndrome develops with irritation of the nerve roots, which is innervated by the membrane (diaphragmatic nerve) or a large chest muscle.The symptoms are definitely the same as the angina pectoris attack, but at the same time the attack is unnaturally long, the pain increases with sharp movement of the head or neck, sharp sneezing or coughing.Standard wreath openings do not bring relief and at the time of the attack the ECG does not show violation of the coronary artery circulation.At the same time, heart syndrome is accompanied by tachicardia, arrhythmia and hypertension. -
Vail artery syndrome
This syndrome is one of the most common and dangerous manifestationsThe cervical region osteochondrosisspine.This syndrome develops in the background of the spinal artery and circulatory disorders in the corresponding areas of the brain (cerebellum, brain and rear lobe), which determines the clinical picture.
One of the main manifestations of spinal arterial syndrome is a strong pulsing and/or burning headache, constant or paroxysmal, exciting darkness, excessive part, whiskey and back of the head.Usually pain can be a side.In the first stages of development, a headache occurs or increases after a long -term stay, back, after physical effort or sudden movements.By narrowing the lumen, the artery of pain becomes more prominent and more frequent, sometimes constant.In severe cases or at the peak of the headache, vomiting may occur, and the state of fainting is not excluded.
Visual disorders with osteochondrosis of the cervix can occur separately and despite the background of the headache, and the pain of the eyeball, the damaged visual acuity, the feeling of veil in front of the eyes, the stove or the stove.One of the typical symptoms of spinal artery narrowing is a sudden short -term attack of dizziness or loss of orientation in space.Such attacks occur for a few seconds and pass quickly.Sudden noise in the ear or pulsation in the head area.In addition, damage to the artery can lead to heart syndrome.
In severe cases, the attack of an "ischemic attack", which can be developed by severe headaches, vomiting, loss of movement coordination, handwriting changes, walking, double thinking, impaired speech and balance, change.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The doctor may make the primary diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervix in the first examination of the patient and determine the level, anatomical characteristics of the affected spine, including posture, body, body structure, spicy side, side corner of the neck;Localization, nature and degree of pain syndrome;The amplitude of the spine, relief and muscle tone.
The diagnosis is determined by visual diagnostic methods (radiographic tests, CT, MRI), which allows the stage of the disease, the level of spine lesions, and the precise localization of the deformed disc.And according to these data, the most optimal treatment of the cervix is chosen.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
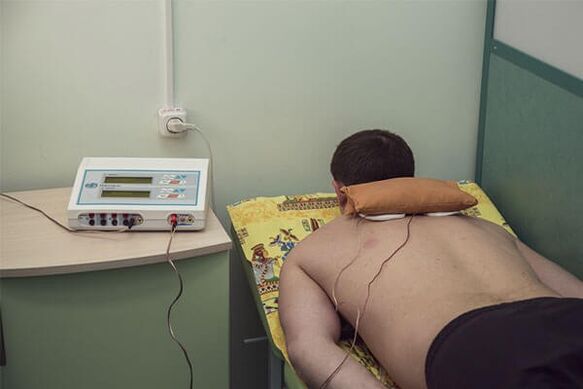
Surgery and conservative methods are used in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervix.However, surgical treatment is prescribed only in the presence of serious complications that occur at later stages of osteochondrosis if:
- Stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal;
- The spine artery is suppressed;
- Significant hernia or protrusion has occurred, which thickens nerve roots;
- Excessive instability of the spine has developed.
In other cases the treatment standardThe cervical region osteochondrosisThe spine is conservative therapy.The reason for this is that with all the results of modern medicine, the consequences of surgical intervention are not always expected.
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervix
The best result in treatmentThe cervical region osteochondrosisThe spine and other types of osteochondrosis can be accessed to a doctor.Unfortunately, many patients often do not affect the mild discomfort of the back or periodic headache.On the other hand, in many cases, there is an inadequate diagnosis and long useless treatment asThe cervical region osteochondrosisThe spine can simulate other diseases such as joint inflammation, myalgia or angina pectoris.This is the reason why spinal fellow spinal control is recommended in the presence of any symptoms of any disease, especially with the head or spinal pain.
The integrated approach is of great importance in effective treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, including the following directions:
- Medication- Improving the trofism of the intervertebral disc and stopping pain, removing muscle cramps and inflammation during aggravation.For these purposes, non -sedoidal anti -inflammatory drugs, analgesics, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors are prescribed to stimulate the restoration of the joints of the joint, multivitamins and group of group B;
- physiotherapy- to reduce pain, to improve the cartilage tissue of the disk, to stimulate cartilage regeneration processes, to remove muscle cramps, to remove inflammatory processes during the postoperative period;
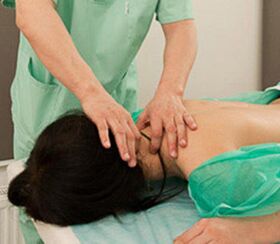
- Manual therapy- Eliminating muscle cramps, reducing pain, improving blood and lymphatic metabolism, improving posture correction, and improving the amplitude of the joints.The manual exposure schema is selected separately for each patient;
- massage-A long-used and well-established method of treating muscle-bone diseases.The same effect as in manual therapy;
- Medical physical educationThis is one of the most important methods to treat all types of osteochondrosis, including osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.The purpose of body exercise is to relieve muscle cramps and compression of nerve roots, improve blood and lymphatic flow in the spine, strengthen the muscle frame and increase the elasticity of the league.We choose a exercise for each patient whose proper implementation is monitored by a specialist;
- reflexologyIt is a widely used alternative treatment today and gives very good results in combination with other treatment methods.The essence of the method is the effect on acupunctural points and/or reflexogenic zones in order to achieve the same results as other therapeutic methods (muscle pain and cramp reduction, decompression of spinal roots, repair of vertebrate tissue trophis), and psychoemotional overlooking.
Chronic osteochondrosis is also used to treat chondroprotectors, Group B (B6, B12) and external use drugs - ointments, creams, gels containing NSAIDs, local riot and tissue regeneration stimulants.
In addition to the main treatment methods, patients are recommended to change the usual lifestyle with the cervical region osteochondrosis, since the disease is mostly low mobility, poor or malnutrition, obesity, or vice versa, the presence of excessive low weight and bad habits.In most cases, in the early stages of cervical osteochondrosis, it is sufficient to conduct a healthy lifestyle, not to overload muscle cramps and the cervical-blinding region, to provide convenient conditions for sleep, normalization of nutrition, and fulfill the doctor's recommendations in physical activity,



















